HENRY CHANGAssociate Professor765-494-0394 LILY 2-223 hcchang@purdue.edu |

|
PROFESSIONAL FACULTY RESEARCH
(Cell and developmental biology) Membrane trafficking; molecular genetics; cell polarity; development; signal transduction.
BIO
We use Drosophila (fruit fly) to investigate developmental mechanisms. There are two main research foci:
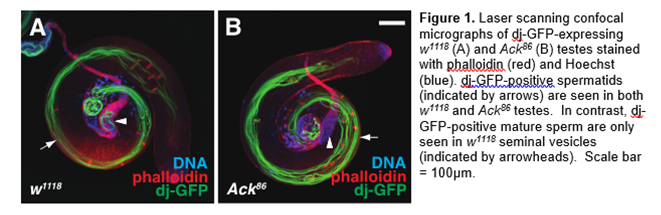
1) To investigate the physiological function of Ack family kinases . The cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase Ack ( A ctivated C dc42 K inase) has the unique capability of directly binding to Cdc42, a small GTPase crucial for cytoskeletal elements, cell polarity, and cell migration. This physical interaction implies that Ack may regulate or facilitate Cdc42-dependent processes. Indeed, aberrant Ack activity has been implicated in promoting metastasis, although the normal functions of Ack family kinases are not well defined. Like mammals, flies have two Ack homologs. We have previously shown that Drosophila Ack recruits Nck adaptor proteins to clathrin-positive structures in male germ cells and is required for male fertility (Figure 1). We are currently investigating the function of Ack-like, the second Ack gene.
Education
B.A. in Biochemical Sciences, Harvard University, 1991
Ph.D. in Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, 1995
Postdoc at Yale University School of Medicine 1997-2004
Selected Publications
Ready, D. F. and H.C. Chang. Calcium waves facilitate and coordinate the contraction of endfeet actin stress fibers in Drosophila interommatidial cells. Development , in press.
Willy, N.M., J.P. Ferguson, A. Akatay, S. Huber, U. Djakbarova, S. Silahli, C. Cakez, F. Hasan, H.C. Chang, A. Travessert, S. Li, R. Zandi, D. Li, E. Betzig, E. Cocucci, and C. Kural. De novo endocytic clathrin coats develop curvature at early stages of their formation. Dev Cell , in press.
Chang, Y.C., Y. X. Peng, P.H. Yu, H. C. Chang, P.S. Liang, T.Y. Huang, C. J. Shih, L.A.Chu, and T.K. Sang. 2021. VCP maintains nuclear size by regulating the DNA damage-associated MDC1–p53–autophagy axis in Drosophila . Nat Comm 12:4258.
Chen, P-L, K-T Huang, C-Y Cheng, J-C Li, H-Y Chan, T-Y Lin, M. Su, W-Y Yang, H.C. Chang, H-D Wang, C-H Chen. 2020. Vesicular transport mediates the uptake of cytoplasmic proteins into mitochondria in Drosophila melanogaster . Nat Comm 11:2592.
Abdallah, A.M., X. Zhou, C. Kim, K.K. Shah, C. Hogden, J.A. Schoenherr, J.C. Clemens, and H.C. Chang. 2013. Activated Cdc42 kinase regulates Dock localization in male germ cells during Drosophila spermatogenesis. Dev. Biol. 378:141-153.
Schoenherr, J.A., J.M. Drennan, J.S. Martinez, M.R. Chikka, M.C. Hall, H.C. Chang, and J.C. Clemens. 2012. Drosophila activated Cdc42 kinase has anti-apoptotic function. PLoS Genet 8(5): e1002725.
Zhou, X., L. Fabian, J.L. Bayraktar, H. Ding, J. Brill, and H.C. Chang. 2011. Auxilin is required for formation of Golgi-derived clathrin-coated vesicles during Drosophila spermatogenesis. Development 138:1111-1120.
Bai, T., J. L. Seebald, K. Kim, H. Ding, D. P. Szeto, and H. C. Chang. 2010. Disruption of zebrafish cyclin G-associated kinase (GAK) function impairs the expression of Notch-dependent genes during neurogenesis and causes defects in neuronal development. BMC Dev. Biol. 10:7.
Kandachar, V. R., T. Bai, and H. C. Chang. 2008. The clathrin-binding motif and the J-domain of Drosophila auxilin are essential for facilitating Notch ligand endocytosis. BMC Dev. Biol . 8:50.
Hagedorn, E. J., J. L. Bayraktar, V. R. Kandachar, T. Bai, D. M. Englert, and H. C. Chang. 2006. Drosophila melanogaster auxilin regulates the internalization of Delta to control activity of the Notch signaling pathway. J. Cell Biol . 173:443-452.
- People
- Faculty
- Staff
- Postdoctoral
- Emeritus